Ntrip Caster Software
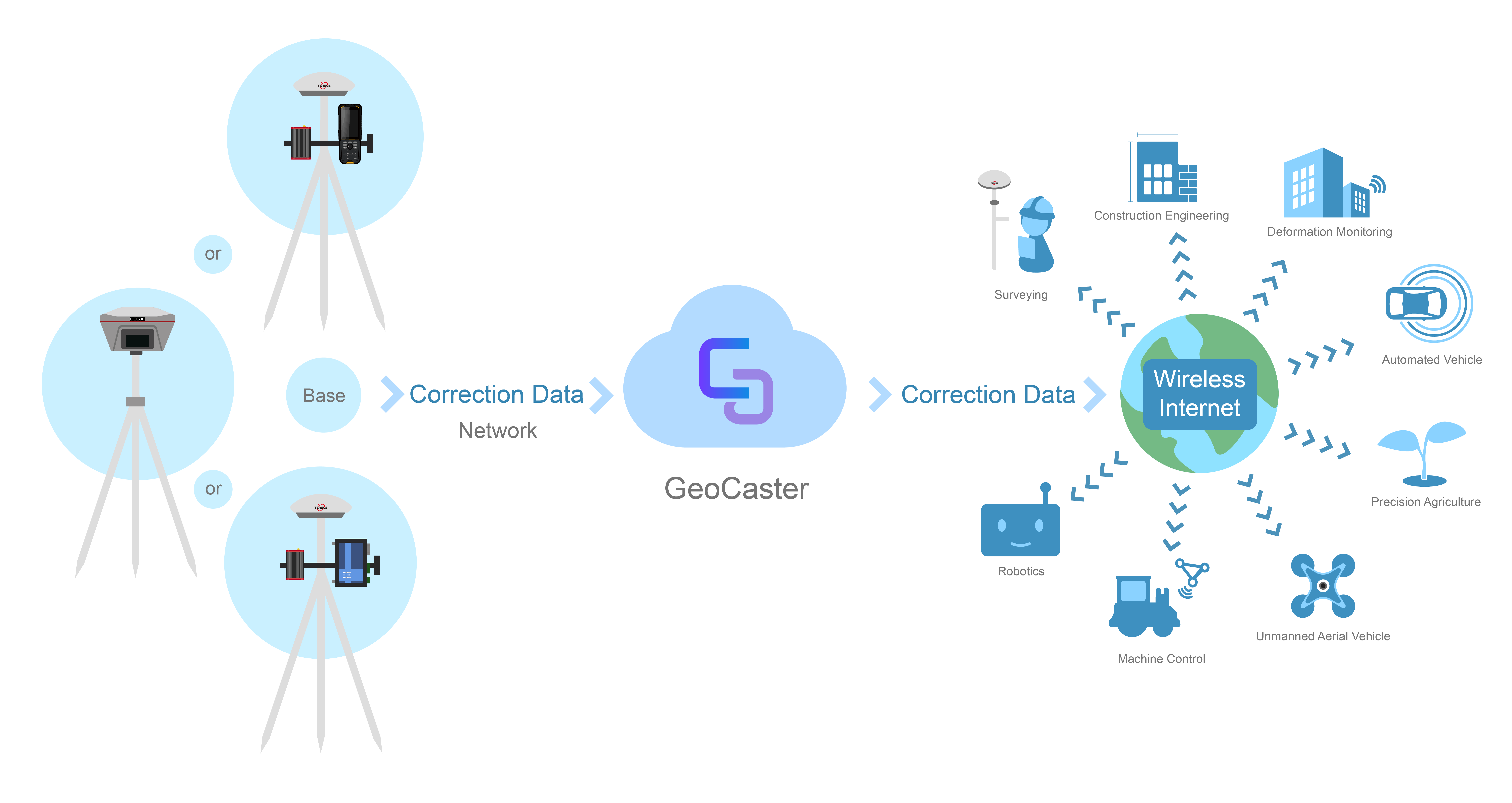
The NTRIP system is made up of three primary software components: caster, server base and client rover. The NTRIP caster is an HTTP Internet service, acting as a line of communication which carries GRSS connection data between NTRIP server and NTRIP clients. From many sources, as seen in the list below. While deploying reference stations (so called NTRIP Servers) can be very costly, and NTRIP Casters other than SNIP often cost thousands, as a rule NTRIP Clients are typically provided for free and can be readily downloaded over the web.
- The Lefebure NTRIP Caster software includes the ability to connect to one serial port and make that data available via on the NTRIP caster. In this scenario, the Caster will commonly live in an office or home, physically close the the base station. There has to be a serial connection between the RTK Base Station and the computer, which means.
- The GNSS Data Management Software (Ntrip) plays an important role in real-time GNSS correction services. Monitoring the availability of the caster server and each individual Ntrip mountpoint is therefore a basic task for service providers. Alberding GmbH offers professional solutions for Ntrip monitoring.
Networked Transport of RTCM via internet protocol, or NTRIP, is an open standard protocol forstreaming differential data over the internet in accordance with specifications published by RTCM.There are three major parts to the NTRIP system: The NTRIP client, the NTRIP server, and the NTRIPcaster:
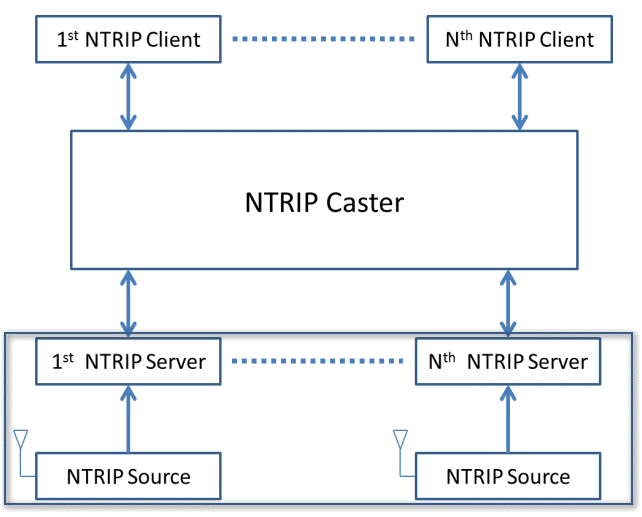
- The NTRIP server is a PC or on-board computer running NTRIP server software communicating directly with a GNSS reference station.
- The NTRIP caster is an HTTP server which receives streaming RTCM data from one or more NTRIP servers and in turn streams the RTCM data to one or more NTRIP clients via the internet.
- The NTRIP client receives streaming RTCM data from the NTRIP caster to apply as real-time corrections to a GNSS receiver.
The EvalTool/CLTool software applications provide NTRIP client functionality to be used with the uINS RTK rover. Typically an EvalTool NTRIP client connects over the internet to an NTRIP service provider. The EvalTool/CLTool NTRIP client then provides the RTCM 3.3 corrections to the uINS and ZED-F9P rover connected over USB or serial. Virtual reference service (VRS) is also supported by the EvalTool/CLTool NTRIP client.
Important
If using a virtual reference service (VRS), the rover must output the NMEA GGA message to return to the NTRIP caster. Without this, the NTRIP caster will not provide correction information.
NTRIP RTCM3 Messages¶
The NTRIP server must provide the necessary subset of RTCM3 messages supported by the uINS-RTK. The following is an example of compatible RTCM3 base output messages provided from a Trimble NTRIP RTK base station.
| Message Type | Period (sec) | Description |
|---|---|---|
| RTCM 1005 | 5 | Stationary RTK reference station ARP |
| RTCM 1007 | 5 | Antenna Descriptor |
| RTCM 1030 | 3 | GPS Network RTK Residual |
| RTCM 1031 | 3 | GLONASS Network RTK Residual |
| RTCM 1032 | 1 | Physical Reference Station Position |
| RTCM 1033 | 5 | Receiver and Antenna Descriptors |
| RTCM 1075 | 1 | GPS MSM5 |
| RTCM 1085 | 1 | GLONASS MSM5 |
| RTCM 1095 | 1 | Galileo MSM5 |
| RTCM 1230 | 5 | GLONASS code-phase biases |
| RTCM 4094 | 5 | Assigned to : Trimble Navigation Ltd. |

Introduction
How are the corrections sent to the rover from the base?
NTRIP Caster Setup | Lefebure
The benefits of using NTRIP over radio setups:
- Less equipment to carry in the field. Almost all data collectors, smartphones, and computers have the capability to connect to the internet even in a field setting. This is usually done through a SIM card.
- No license required (some radios require licensing).
- Mitigate the chance of radio interference.
- No limitation on communication range. 900MHz, VHF, and UHF radios have a limited range.
The limits of using NTRIP:
- Requires the work area is in range of cellular service for receiving corrections data via the Internet.
How does NTRIP work?
